Types and Working of Marine Boiler – Principle of working
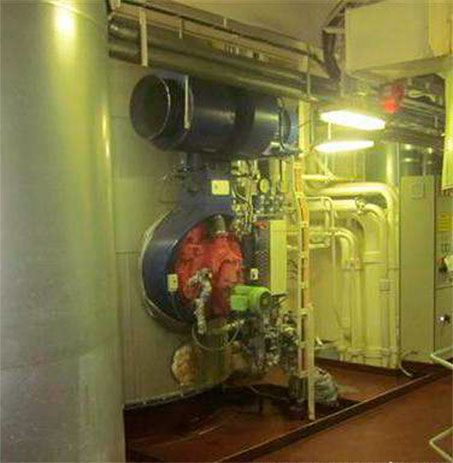

Boiler is one such machinery, which is being used on board ships from the very early days of shipping when there were no propulsion or power generating auxiliary engines.
During that time, boiler was used to do all the major works on ships that present day propulsion and power generating systems do. With evolution of technology, a variety of machines took over the important jobs on ships; however, advanced boilers are still an important part of the engine power plant and cargo operations.
Considering their functionality, the material used for the construction of boilers must be such that they can withstand the immense steam pressure and extreme temperature with minimum heat loss to the surroundings.
Normally, carbon steel is used for the construction of pressure vessels, which are manufactured by open hearth, electric or pneumatic processes. An important point to be considered for boiler construction is that the strength of the material used is tested as per the regulatory requirements.
Principle of Working: The marine boiler works on a simple principle of change in state of water from liquid to vapor form by utilizing the heat energy. The water is boiled in an enclosed pressure vessel so that the steam generated is not lost to the atmosphere. The heating source is enclosed in an insulated furnace to ensure that the heat energy is transferred mainly to the water and not to surrounding area.
A variety of boilers are used on ships, depending upon their size and type. The most common types of boiler installed on board are:
Smoke Tube Boiler
As the name suggests, the heated smoke generated in the boiler furnace is passed through several tubes surrounded by water in the boiler drum.
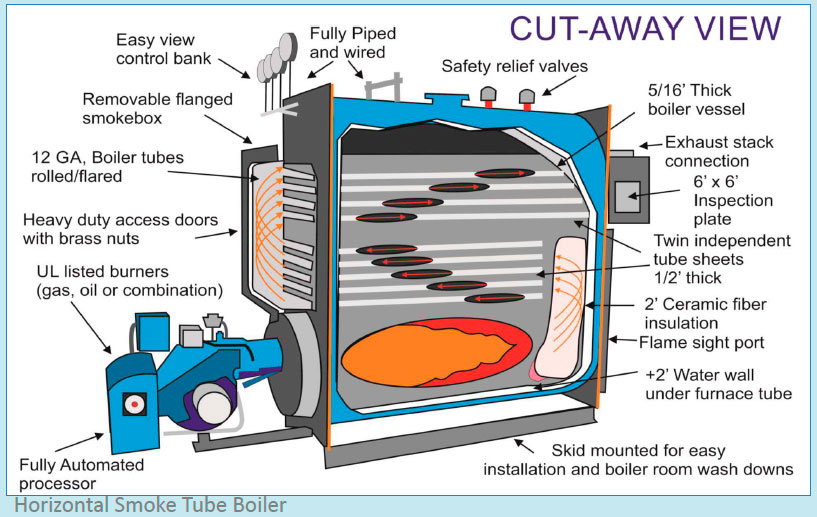
The heat of the smoke in the tubes generates the steam. The smoke tube boilers are used in a system with less steam quantity and quality. In a ship, a smoke tube boiler can be described as – horizontal or scotch boiler and vertical smoke tube boiler
Horizontal Smoke Tube or Scotch Boiler: This is an old type of boiler with cylindrical furnace surrounded by water inside the shell. The furnace in this type of boiler is water-cooled, has a large diameter, and is thicker. This leads to thermal stresses if the boiler is not operated correctly.
Horizontal smoke tube boiler comprises of end plates, which are opposite to the burner assembly. These flat-ended plates, supported by large steam space, stay in the upper portion of the boiler. The combustion chamber is supported by the girder stay at the topside and by the combustion chamber stays. The mid-section back plates and tube plates are also supported by the combustion chamber stays.
Vertical Smoke Tube Boiler: A vertical smoke tube boiler is more popular and commonly found on ships. In this boiler arrangement, the furnace is in the bottom part of the boiler and is attached to the shell by means of ogee ring at the bottom.
The furnace is fitted with refractory, which contains the produced heat inside the furnace and also protects the ogee ring from overheating. The combustion chamber with tube stacks is located above the furnace, where the hot smoke is passed for heating the water drum. The top of the combustion chamber is supported by gusset plate that transfers the stresses to boiler shell.
Fire tube boilers are competitive for steam rates up to 12,000 kg/hour and pressures up to 18 kg/cm2. Fire tube boilers are available for operation with oil and gas fuels.
Water Tube Boiler
Water tube boilers are 2nd generation boilers with modification in the construction and working principle of the smoke tube boiler. The tubes inside the boilers are filled with water instead of smoke and hence the thermal stresses are less as compared to those produced by the smoke tube boiler.
This type of boiler is used where the steam quality and quantity demand is high. All high pressure boilers are mainly water tube boilers and comprise of mainly 3 important sections:
Water drum Steam drum TubesWater drum: It is located at the bottom of the boiler and carries the hot water. The same water is supplied to the steam drum where the steam is generated.
Steam drum: It is located at the top part of the boiler and is fitted with external and internal mountings, which include safety valves and steam stop valves (main and auxiliary), to supply steam to the ship’s systems.
Tubes: Modern water tube boiler consists of various types of water tubes with different functions. The main types are:
Screen tubes: Placed before the super-heater, these tubes are adjacent to the furnace and absorb the flame as well as the generated hot gas heat. Since these tubes are directly exposed to the furnace heat, they are of large diameter to prevent overheating Superheater tubes: They are placed behind the screen tubes to carry the superheated steam from the boiler Generating tubes: These tubes connect the water drum and the steam drum. As the name suggests, hot water is carried upward from water drum to steam drum where the steam is produced Down comers: Down comer tubes transfer the not-so-hot water to the water drum, where the water is heated up in the generating tube before going back to the steam drum
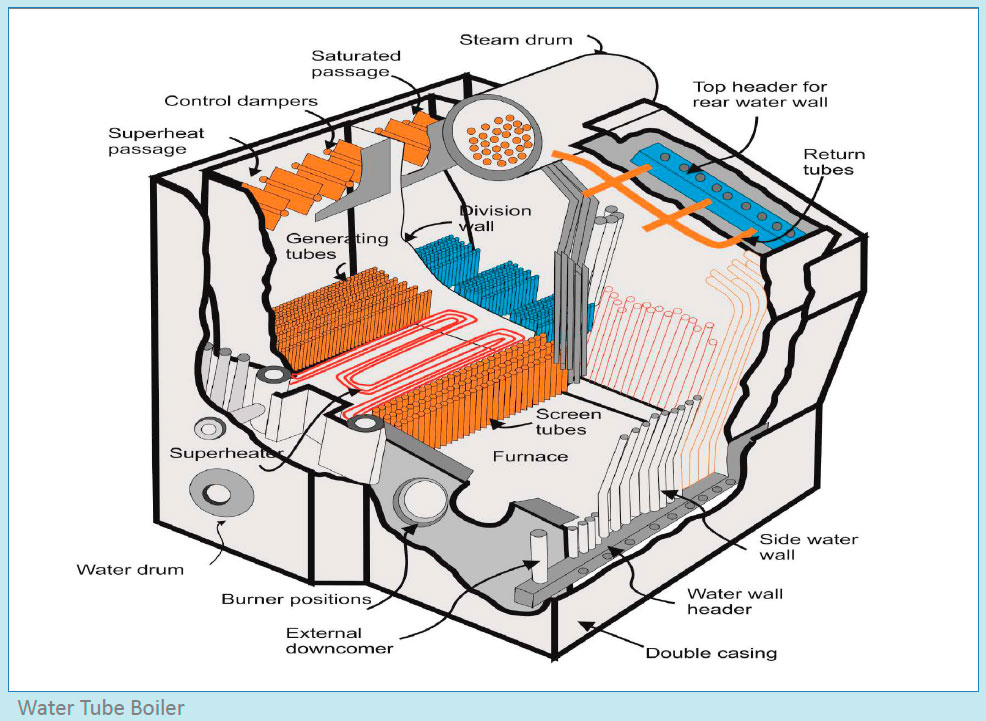
Working Principle of Water Tube Boiler: The Water Tube boiler works on the principle of convection and radiation.
Most modern water tube boiler designs are within the capacity range 4,500 – 120,000 kg/hour of steam at very high pressures. Many water tube boilers are of “packaged” construction in case oil and /or gas are to be used as fuel.
The main features of water tube boilers are
Forced, induced and balanced draft provisions help to improve combustion efficiency Less tolerance for water quality calls for water treatment plant Higher thermal efficiency levels High pressure ratings Better quality of steam Suitable for large capacity systemExhaust Gas Boiler
The exhaust gas boiler and economizer are heat recovery units and types of water tube boiler. The flue gases from the exhaust of the engine are used to heat water in the tubes at a specific temperature and limited pressure loss.
A circulation pump is used to continuously circulate the hot water in the water tubes of the economizer.
The auxiliary steam boiler serves as a steam separator for the entire system and is thus kept hot and ready to start instantly.
The excess steam produced by the economizer when the main engine is running at high load, is dumped back to the hot-well using a steam dump condenser.
The exhaust boiler is provided with a vertical register of double steel tubes having steel gills welded on the tube. This provides a strong rigid structure and also assists in preventing damages caused by vibrations.
Since hot gases flows from the boiler trunk to heat up the water, the complete exhaust boiler is prone to thermal expansion, which is controlled by fitting various tubes and plates.
Tube register, tube support and tube bends are placed in the flow direction of the exhaust gases. The tube supports are fixed at one side of the inlet and outlet header to a supporting beam. The other end is kept free of supporting beam to accommodate for the thermal expansion.
The boiler foundation is provided with footplates, which also support the structure and absorbs the thermal expansion. For additional strengthening and support, stays are fitted on topside with lifting eyes bolted to the steel structure.
Composite Boiler
Another most common type of boiler found on ships is the composite boiler, where the exhaust heat of the main engine or generator engine is used to additionally heat the water or generate the steam. Technically, composite boiler is an integration of exhaust gas boiler and oil-fired boiler.
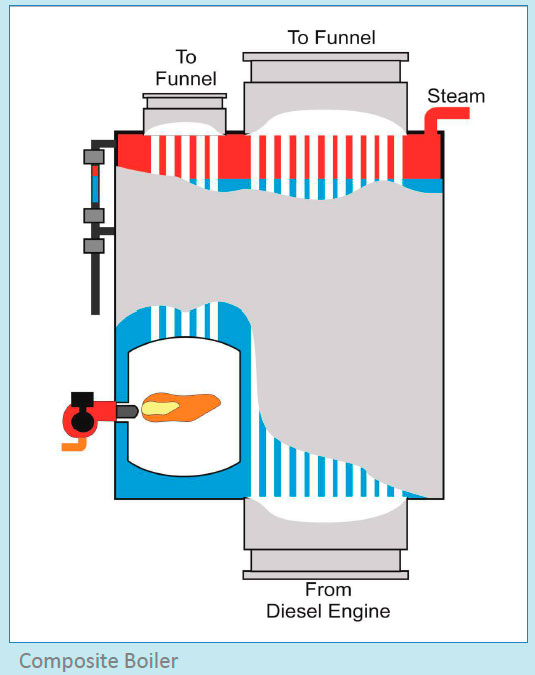
A composite boiler can be a water tube or a smoke tube boiler divided in two different sections. One section of the boiler is heated by the burner and the other by the exhaust gases produced by ship’s engine.
Difference Between Smoke and Water Tube Boilers
Smoke Tube Boiler Water Tube Boiler Suitable for low pressure range Suitable for high pressure range – 100 bars High thermal stresses Low thermal stresses Low quality and quantity of steam High quality and quantity of steam Less efficient Highly efficient Large diameter tube Small diameter tube Heavy in weight Light in weight for same capacity Risk of explosion is less Risk of explosion is highReferences
A Guide to Boiler Operation and Maintenance Construction and Design. Anish Wankhede [2015]